Image Recognition + ID: Google Cloud Vision API, ClickSend
Just like people, dogs are scared by all kinds of things. Most often, it’s a result of having a negative experience or not being handled when their natural fears surface. In this example, we'll create a way to make sure your dog is safe when you are away.
You can attach a camera to the collar of your dog that can capture images and use Vision API for detection and recognition of the image. Let's say your dog is scared of cats and you want to make sure your little furry friend is safe from cats while playing in the backyard in your absence. You could build an application where you could get SMS alerts to your device when cats are recognized by Cloud Vision API.
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to recognize an image using Google Cloud Vision API and alert the user with an SMS using ClickSend API. PubNub forms the skeleton of the application and interconnects the features.
The full project GitHub repo is available here.
Let's Get Building
Assume your laptop's webcam is the camera fixed to your dog's collar. Below is the code that opens your webcam and takes pictures for you. You could set time interval to capture images frequently. These images go into a canvas element and can be saved it into your device. You can find the code for clicking and saving of the images below.
(function() {
var video = document.getElementById('video');
var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas');
var context = canvas.getContext('2d');
var vendorUrl = window.URL || window.webkitURL;
var photo = document.getElementById('photo');
navigator.getMedia = navigator.getUserMedia ||
navigator.webkitGetUserMedia ||
navigator.mozGetUserMedia ||
navigator.msGetUserMedia;
navigator.getMedia({
video: true,
audio: false
}, function(stream) {
video.src = vendorUrl.createObjectURL(stream);
video.play();
}, function(error) {
//error
});
document.getElementById("capture").addEventListener("click",function(){
context.drawImage(video,0,0,400,300);
photo.setAttribute('src',canvas.toDataURL('image/jpeg',0.7));
});
document.getElementById("save").addEventListener('click', function(e) {
this.href = document.getElementById('canvas').toDataURL();
this.download = 'my-file-name.jpeg';
});
})();
Cloud Vision API
The Google Cloud Vision API enables developers to understand the content of an image through its powerful machine learning models. To get started with implementing the Vision API, you need to create a new project here. Before you create a new project you need to set up your billing account. After this, you need to enable Vision API.
For more details, check this quickstart link.
Run the following command on your terminal:
pip install --upgrade google-cloud-vision
To run the client library, you must first set up authentication by creating a service account here and setting an environment variable.
- From the Service account drop-down list, select the New service account.
- Enter a name into the Service account name field.
- Do not select a value from the Role drop-down list. No role is required to access this service.
- Click Create. A note appears, warning that this service account has no role.
- Click Create without role. A JSON file that contains your key downloads to your computer.
Now set the environment variable GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS to the file path of the JSON file that contains your service account key. This can be done as follows:
For Linux/Mac OS:
export GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS="[PATH]"
For Windows:
set GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS=[PATH]
Now you are all ready to run your code that recognizes your image. Here's the Python code that takes the snapshots from the directory where you have saved them (Mine is Downloads) and responds with labels.
import io
import os
from google.cloud import vision
from google.cloud.vision import types
client = vision.ImageAnnotatorClient()
file_name = os.path.join(
os.path.dirname(__file__),
'/Users/namratha/Downloads/my-file-name.jpeg')
with io.open(file_name, 'rb') as image_file:
content = image_file.read()
image = types.Image(content=content)
response = client.label_detection(image=image)
labels = response.label_annotations
for label in labels:
if "cat" not in label.description:
output = 'no'
else:
output = 'yes'
break
The result of image recognition is sent to the user using PubNub Real-time Messaging. User's device is made to subscribe to a channel, say, alert_notify to which Vision API's result of image recognition is sent.
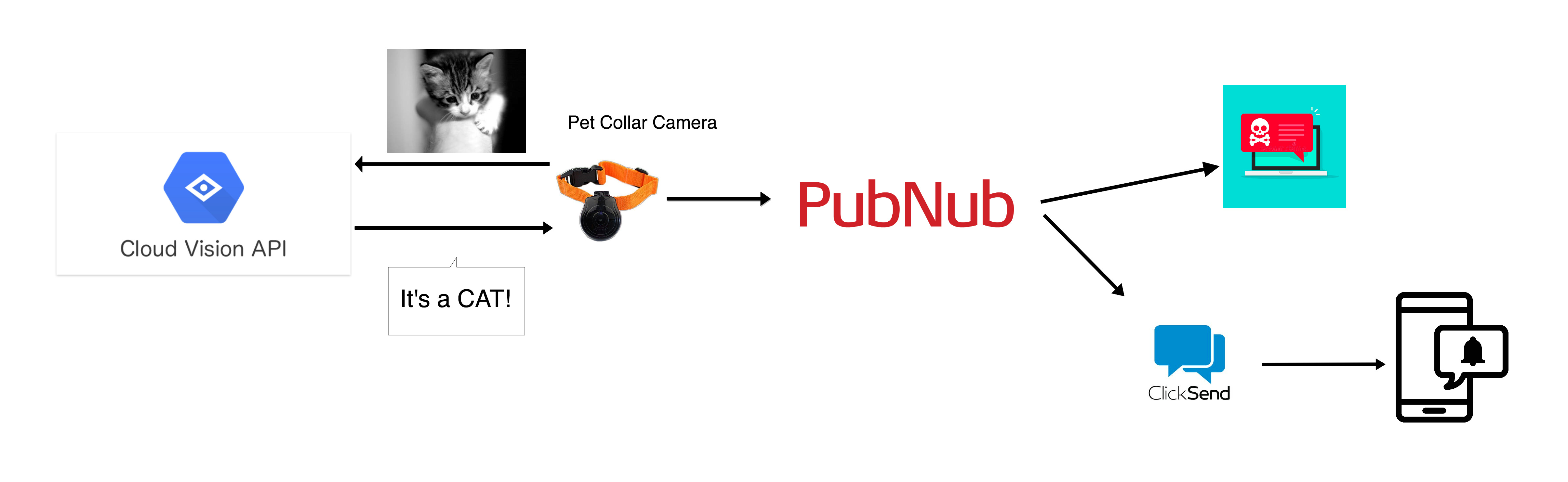
Web Notification Alert using PubNub
You'll now have to initialize your PubNub keys. Sign up for a PubNub account and create a project in the Admin Dashboard.
var pubnub = new PubNub({
publish_key: 'Enter your publish key here',
subscribe_key : 'Enter your subscribe key here'
});
pubnub.addListener({
message: function(message) {
notifyMe(message.message);
chatSend(message.message);
}
})
pubnub.subscribe({
channels: ["alert_notify"]
});
Now you can publish the alert message inside your Python code which you can send as a web push notification to your device. The device, in turn, subscribes to alert_notify channel and receives the alert message from your camera.
if status.category == PNStatusCategory.PNConnectedCategory:
if output is 'yes':
pubnub.publish().channel('alert_notify').message('Cat!').async(my_publish_callback)
You can design the web push notification using Notification API in HTML5.
function notifyMe(message) {
if (message == undefined){
message = "Alert! Unable to recognize";
};
if (!("Notification" in window)) {
alert("This browser does not support desktop notification");
} else if (Notification.permission === "granted") {
var notification = new Notification(message);
} else if (Notification.permission !== 'denied') {
Notification.requestPermission(function (permission) {
if (permission === "granted") {
var notification = new Notification("Hi there!");
}
});
}
}
ClickSend API
ClickSend API allows developers to integrate SMS, voice, fax, post or email into their applications. You could send an SMS to your mobile device along with web push notification using PubNub. ClickSend API is well-documented for developers.
We used ClickSend's HTTP API. So everytime Vision API recognizes an image, you get an SMS to your device.
function chatSend(message) {
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
var username = 'Enter your ClickSend username here';
var key = 'YOUR_CLICKSEND_API_KEY';
var number = 'Enter your number here';
request.open('POST', 'https://api-mapper.clicksend.com/http/v2/send.php');
request.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
request.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (this.readyState === 4) {
console.log('Status:', this.status);
}
};
var body = "username="+username+"&key="+key+"&to="+number+"&message=" + message;
request.send(body);
}
This is a great starting point for building applications using different APIs and connecting them through PubNub.