Data Security
PubNub is serious about the security of your data. Using TLS and AES256 encryption algorithms, and with CCPA, GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2 type II, SOC 3, and ISO 27001 compliance, you can be sure your data is safeguarded.
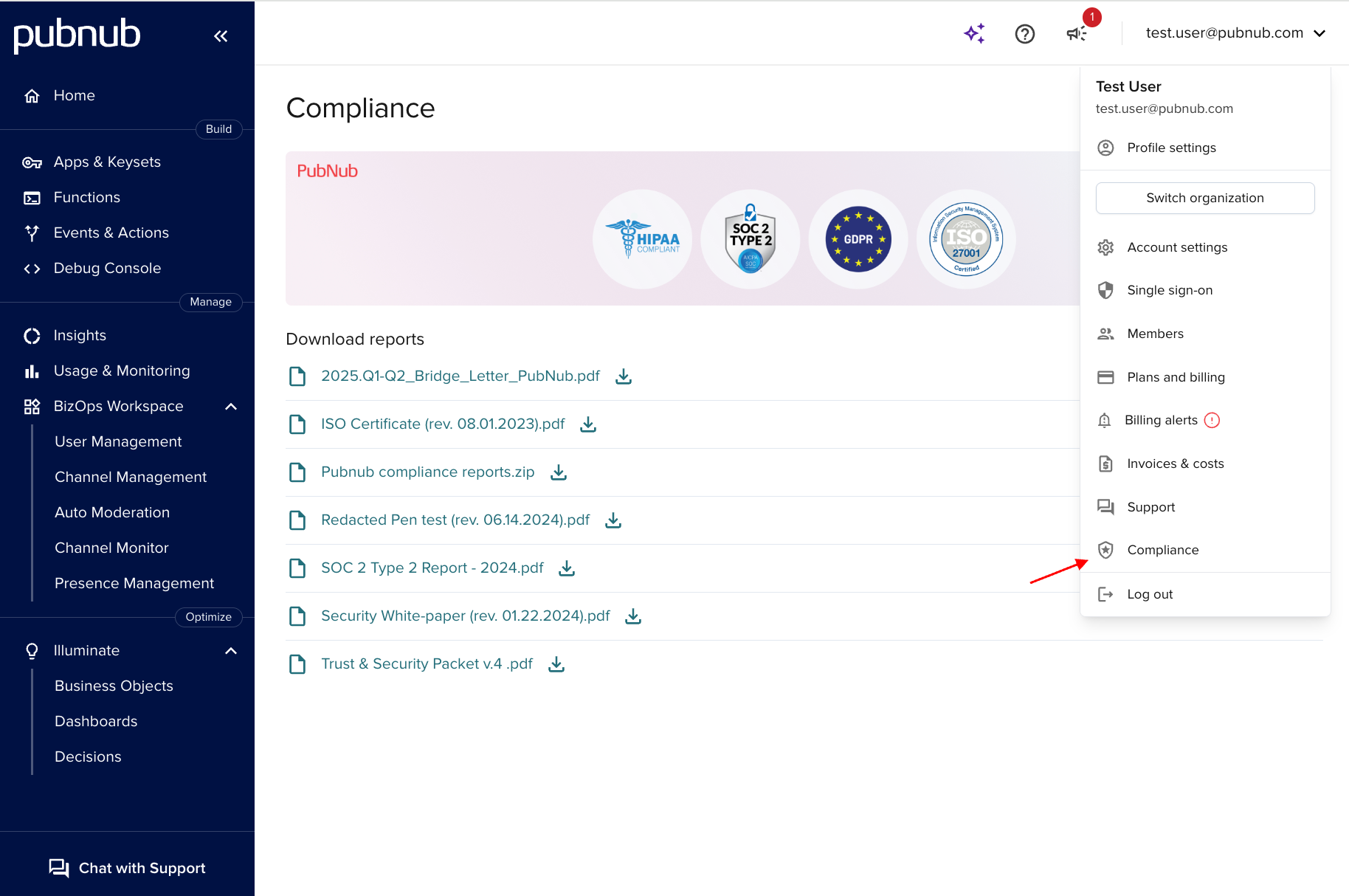
Compliance reports
If you are a Pro customer, you can access the most recent versions of the SOC2 type II and SOC 3 and other compliance reports directly from the Admin Portal. If you’re not a Pro customer, contact PubNub Compliance.
There are several ways in which PubNub helps to secure your app:
- Connection security secures the traffic between your client and PubNub
- Message encryption provides end-to-end security for every message, in transit and at rest
- File encryption provides end-to-end security for every file you upload, in transit and at rest
- Access management provides a detailed permission schema for your app
User ID / UUID
User ID is also referred to as UUID/uuid in some APIs and server responses but holds the value of the userId parameter you set during initialization.
Connection security
PubNub offers connection level security through TLS Encryption (Transport Layer Security). It's enabled by default and generally there is no reason to disable it for any production application.
TLS version
Connections to PubNub APIs are encrypted using TLS 1.2, which provides secure communication over HTTPS between clients and PubNub servers.
Configuring TLS
TLS is enabled by default. If you need to disable it for any reason, it can be done during the PubNub object initialization.
SSL
Some PubNub SDKs, the parameter name is ssl (a legacy name for TLS) but it represents the latest connection encryption technology available. SSL v3 was deprecated due to a security exploit that was discovered and TLS was developed to replace it as the industry standard. Many will refer to TLS as SSL out of habit.
- JavaScript
- Swift
- Objective-C
- Java
- C#
- Python
1var pubnub = new PubNub({
2 subscribeKey: "mySubscribeKey",
3 publishKey: "myPublishKey",
4 userId: "myUniqueUserId",
5 ssl: false // default 'true'
6});
1import PubNubSDK
2
3let config = PubNubConfiguration(
4 publishKey: "demo",
5 subscribeKey: "demo",
6 userId: "myUniqueUserId",
7 useSecureConnections: false // default true
8)
9
10let pubnub = PubNub(configuration: config)
1PNConfiguration *pnconfig = [PNConfiguration configurationWithPublishKey:@"myPublishKey"
2 subscribeKey:@"mySubscribeKey"];
3
4pnconfig.uuid = "theClientUUID"
5pnconfig.TLSEnabled = NO; // default YES
6self.client = [PubNub clientWithConfiguration:pnconfig];
1PNConfiguration.Builder configBuilder = PNConfiguration.builder(new UserId("yourUserId"), "yourSubscribeKey");
2// publishKey from Admin Portal (only required if publishing)
3configBuilder.publishKey("PublishKey");
4configBuilder.secure(false);
5PubNub pubNub = PubNub.create(configBuilder.build());
1PNConfiguration pnConfiguration = new PNConfiguration(new UserId("myUniqueUserId"));
2pnConfiguration.PublishKey = "myPublishKey";
3pnConfiguration.SubscribeKey = "mySubscribeKey";
4pnConfiguration.Secure = false; // default true
5
6Pubnub pubnub = new Pubnub(pnConfiguration);
1from pubnub.pnconfiguration import PNConfiguration
2from pubnub.pubnub import PubNub
3
4pnconfig = PNConfiguration()
5pnconfig.publish_key = "myPublishKey"
6pnconfig.subscribe_key = "mySubscribeKey"
7pnconfig.user_id = "myUserID"
8pnconfig.ssl = False # default True
9
10pubnub = PubNub(pnconfig)
TCP connection troubleshooting
If you need to capture the TCP traffic (a tcpdump to a .pcap file) to analyze and debug the network traffic, you may need to disable TLS in your development environment. This level of analysis is only necessary to troubleshoot the most difficult network connection and communication issues that are typically outside of the PubNub domain.
Custom domain
You might want to use your own domain name for client applications to access PubNub’s real-time messaging infrastructure instead of the default PubNub endpoint ps.pndsn.com.
The reasons can include:
- Branding – a custom domain helps maintain a consistent and professional brand image across all your services and interactions by making your application's traffic appear under your own domain
- Compliance and control – you may have legal or regulatory requirements to use custom domains for data management, offering more control over how data is accessed and tracked.
- Infrastructure integration – for better integration with the existing security, CDN, or networking infrastructure, optimizing your overall system configuration.
- Traffic management – a custom domain allows PubNub to route traffic per customer efficiently, mainly when a point of presence (PoP) is underperforming or unavailable, improving performance and reliability.
Secure connections
Ensure connections are made over HTTPS instead of HTTP. HTTPS ensures a secure network by encrypting data and protecting your client data by preventing man-in-the-middle attacks.
If you are a paid customer, you can submit a request to PubNub support and have the custom domain (a.k.a. origin) configured for you.
PubNub also provides TLS certificate hosting if required. When TLS is used, you must supply us with your own certificate. This service comes with an additional monthly fee.
Request process
To request a custom domain, contact PubNub support by raising a support ticket entitled "Request Custom Origin" and providing the following details in the request:
- The PubNub account email that has or will have the paid production keyset(s).
- Three choices for your subdomain in order of preference (12 characters or less, like
abc.pubnubapi.com). - PubNub SDKs you currently use in your applications: SDK language/name and version.
- If you have customers or devices in China, mention it in the request.
PubNub support will confirm your custom origin name and SDK initialization code for the SDK/version you use.
Once you have it, you can start using it by changing the way you initialize a PubNub instance in your SDK (with the origin parameter).
Connection limits
To improve response times and avoid congestion, browsers have their own limitations to concurrent connections:
| Browser | Connections per host name | Max connections |
|---|---|---|
| Chrome | 6 | 10 |
| Chrome mobile | 6 | 16 |
| Internet Explorer 9 | 6 | 35 |
| Internet Explorer Mobile 9 | 6 | 60 |
| Internet Explorer 10 | 8 | 17 |
| Internet Explorer 11 | 13 | 17 |
| Firefox | 6 | 17 |
| Safari | 6 | 17 |
| Android | 6 | 17 |
Message encryption
PubNub SDKs allow you to configure the encryption/decryption algorithms using pre-bundled packages for encrypting/decrypting data (cryptors) in your apps through crypto modules.
Crypto module
A crypto module contains cryptors that encrypt and decrypt data in your app. You can choose the algorithm:
- Legacy 128‑bit (legacy module)
- Recommended AES‑CBC 256‑bit (CBC mode)
Compatibility:
- Current SDKs can decrypt content from either module.
- Legacy 128‑bit and AES‑CBC 256‑bit can read each other’s content.
- You can switch to AES‑CBC 256‑bit and still read historical and older‑client messages.
Legacy encryption with 128-bit cipher key entropy
You don't have to change your encryption configuration if you want to keep using the legacy encryption. If you want to use the recommended 256-bit AES-CBC encryption, you must explicitly set that in PubNub config.
If you do not explicitly select either module in your app and have cipherKey and, optionally, useRandomInitializationVector set in PubNub configuration, the client defaults to using the legacy encryption.
For information on how to configure modules, refer to the Configuration documentation of each SDK.
Keep your clients up to date
Apps not using the latest SDK version will not be able to decrypt data encrypted using the 256-bit AES-CBC cipher. Make sure to update your clients or encrypt data using the legacy module.
Upgrade to 256-bit encryption
For information on how to migrate to the recommended encryption algorithm, refer to 256-bit AES-CBC Encryption.
Encryption scope
Depending on whether you want to encrypt all messages and files or just some of them, create and register a crypto module differently.
-
To fully encrypt every message and file in all channels for a given API key, specify and register the crypto module as part of the PubNub configuration when you create the object.
-
To only encrypt some or partially encrypt messages, do not specify the crypto module as part of the PubNub configuration. Instead, create a standalone instance of a crypto module and call one of the available
encrypt()ordecrypt()methods.
Encrypting messages
To configure encryption for all messages and files in all channels for a given API key, you need to register a module, provide a cipherKey, and, optionally, decide whether to use a random initialization vector to encrypt (and decrypt) data.
For information on partial encryption, refer to the Partial Message Encryption section.
- JavaScript
- Swift
- Objective-C
- Java
- Go
- Kotlin
- Rust
- Ruby
- Dart
- C#/Unity
1var pubnub = new PubNub({
2 ...
3 // all necessary config options
4 cryptoModule: PubNub.CryptoModule.aesCbcCryptoModule({cipherKey: 'pubnubenigma'})
5});
1let pubnub = PubNub(
2 configuration: PubNubConfiguration(
3 ...
4 // all necessary config options
5 cryptorModule: CryptorModule.aesCbcCryptoModule(with: "pubnubenigma")
6 )
7)
1...
2// all necessary config options
3config.cryptoModule = [PNCryptoModule AESCBCCryptoModuleWithCipherKey:@"enigma"
4 randomInitializationVector:YES];
1
1config := pubnub.NewConfigWithUserId(UserId("myUniqueUserId"))
2// all necessary config options
3config.CryptoModule = crypto.NewAesCbcCryptoModule("cipherKey", true)
4
5pn := pubnub.NewPubNub(config)
1
1let client = PubNubClientBuilder::with_transport(Transport)
2 ...
3 // all necessary config options
4 .with_cryptor(CryptoModule::new_aes_cbc_module("enigma", true)?)
5 .build()?;
1pubnub = Pubnub.new(
2 ...
3 # all necessary config options
4 crypto_module: Crypto::CryptoModule.new_aes_cbc("enigma", true)
5)
1final pubnub =
2 PubNub(
3 ...
4 // all necessary config options
5 crypto: CryptoModule.aescbcCryptoModule(CipherKey.fromUtf8('enigma'));
6 );
1PNConfiguration pnConfiguration = new PNConfiguration(new UserId("myUniqueUserId"));
2...
3// all necessary config options
4pnConfiguration.CryptoModule = new CryptoModule(new AesCbcCryptor("enigma"), new List<ICryptor> { new LegacyCryptor("enigma") })
5
6new PubNub(pnConfiguration);
The SDK encrypts each message before publish. The network routes only encrypted data. The message stays encrypted until it reaches the subscribing client.
The subscriber decrypts it with the same cipher key. Data stored in Message Persistence (and logging systems) remains encrypted. Only clients with the cipher key can decrypt it.
Protect your cipher key
You shouldn't share the cipher key outside of the PubNub network.
Partial message encryption
Sometimes encrypting only part of the payload makes sense. With Mobile Push Notifications, push services must read specific keys and values. Encrypt only sensitive fields and leave push-related fields as clear text.
Create a separate crypto module instance and call encrypt() or decrypt() on that instance.
APNs example
This example shows how to encrypt only the results object in an APNs payload.
Before encryption:
1{
2 "pn_apns": {
3 "aps": {
4 "alert": "Your test results are available.",
5 "sound" : "bingbong.aiff"
6 }
7 },
8 "results": {
9 "test_name": "pregnancy",
10 "results": "positive",
11 "notes": "You are having twins!"
12 }
13}
Encrypt it:
Only the results object must be encrypted. Other fields can remain plain text.
- JavaScript
- Swift
- Objective-C
- Java
1const clearText = JSON.stringify(
2 {"test_name":"pregnancy","results":"positive","notes":"You are having twins!"});
3
4// create a crypto module instance
5const cryptoModule = PubNub.CryptoModule.aesCbcCryptoModule({
6 cipherKey: "pubnubenigma"
7});
8
9const secureText = cryptoModule.encrypt(clearText);
1let clearData = [
2 "test_name":"pregnancy",
3 "results":"positive",
4 "notes":"You are having twins!"
5]
6
7do {
8 let cryptoModule = CryptoModule.aesCbcCryptoModule(with: "pubnubenigma")
9 let encryptedMessage = try cryptoModule.encrypt(data: try JSONEncoder().encode(clearData)).get()
10} catch {
11 // ...
12}
1PNCryptoModule *aesCBCCrypto = [PNCryptoModule AESCBCCryptoModuleWithCipherKey:@"enigma" randomInitializationVector:YES];
2
3NSString *message = @"You are having twins!";
4NSData *messageData = [message dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
5
6NSData *encryptedWithAESCBC = [aesCBCCrypto encrypt:messageData];
1
You can now add the secureData variable to the payload so that PubNub and third party mobile push vendors can process the Push payload correctly.
Using a 32‑character cipher key for AES‑256, the resulting message payload is as follows.
After encryption:
1{
2 "pn_apns": {
3 "aps": {
4 "alert": "Your test results are available.",
5 "sound" : "bingbong.aiff"
6 }
7 },
8 "results": "Nio2At2uvQzteLoSqznLkZQ3dlFlMzLGlUwbsMndZ7/7tllq2joJw6WcUv3XpMdEugYRnoEvsrlhEVkSnBibxaxDDWMFEDvKS+VLlA8mfmg="
9}
Partial Message Encryption
You may need to encrypt certain data values within the APNs/FCM payload, but be sure not to encrypt any APNs/FCM keys, or any values that need to be parsed as unencrypted text by those mobile push services.
Decrypting messages
On the receiver, use the same crypto module and cipher key to decrypt the encrypted parts of the payload.
- JavaScript
- Swift
- Objective-C
- Java
1// parse the received message and pass the encrypted parts to decrypt API.
2const secureText =
3 "Nio2At2uvQzteLoSqznLkZQ3dlFlMzLGlUwbsMndZ7/7tllq2joJw6WcUv3XpMdEugYRnoEvsrlhEVkSnBibxaxDDWMFEDvKS+VLlA8mfmg="
4
5const clearData = pubnub.decrypt(secureText);
1// parse the received message and pass the encrypted parts to decrypt API
2let secureText =
3 "Nio2At2uvQzteLoSqznLkZQ3dlFlMzLGlUwbsMndZ7/7tllq2joJw6WcUv3XpMdEugYRnoEvsrlhEVkSnBibxaxDDWMFEDvKS+VLlA8mfmg="
4
5do {
6 let clearData = try pubnub.decrypt(data: Data(base64Encoded: secureText) ?? Data()).get()
7} catch {
8 // ...
9}
1PNCryptoModule *aesCBCCrypto = [PNCryptoModule AESCBCCryptoModuleWithCipherKey:@"enigma" randomInitializationVector:YES];
2PNCryptoModule *aesCBCCrypto = [PNCryptoModule AESCBCCryptoModuleWithCipherKey:@"enigma" randomInitializationVector:YES];
3
4// parse the received message and pass the encrypted parts to decrypt API
5
6NSString *secureText =
7 @"Nio2At2uvQzteLoSqznLkZQ3dlFlMzLGlUwbsMndZ7/7tllq2joJw6WcUv3XpMdEugYRnoEvsrlhEVkSnBibxaxDDWMFEDvKS+VLlA8mfmg="
8
9NSData *secureData = [[NSData alloc] initWithBase64EncodedString:secureText options:0];
10NSString *clearData = [aesCBCCrypto decrypt:secureData];
1
For more examples of decrypting messages in other languages, refer to the Configuration and/or Miscellaneous documentation of each SDK.
File encryption
You can also encrypt files with a crypto module.
If you registered a crypto module in configuration, you don't need to pass it when encrypting or decrypting uploaded files.
Do not pass cipher key
Passing a cipher key in sendFile or downloadFile overrides the crypto module configuration and uses legacy 128‑bit encryption.
Refer to Encrypting Messages for information on how to configure the crypto module.
With client‑side encryption, the SDK encrypts file data before upload. The receiving client decrypts the data on download using the same key before it is displayed in the end‑user application.
Encrypting files
The following shows how to encrypt a file using the crypto module registered in PubNub config.
- Node.js
- C#
- Go
- Objective-C
- Java
1 import fs from 'fs';
2
3 const myFile = fs.readFileSync('./cat_picture.jpg');
4
5 const result = await pubnub.sendFile({
6 channel: 'my_channel',
7 message: 'Look at this photo!',
8 file: { data: myFile, name: 'cat_picture.jpg', mimeType: 'application/json' }
9 });
1PNResult<PNFileUploadResult> fileUploadResponse = await pubnub.SendFile()
2 .Channel("my_channel")
3 .File("cat_picture.jpg") //checks the bin folder if no path is provided
4 .Message("Look at this photo!")
5 .ExecuteAsync();
6PNFileUploadResult fileUploadResult = fileUploadResponse.Result;
7PNStatus fileUploadStatus = fileUploadResponse.Status; // contains troubleshooting info
8if (!fileUploadStatus.Error && fileUploadResult != null) // checks if successful
9{
10 Console.WriteLine(pubnub.JsonPluggableLibrary.SerializeToJsonString(fileUploadResult));
11}
12else
13{
14 Console.WriteLine(pubnub.JsonPluggableLibrary.SerializeToJsonString(fileUploadStatus));
15}
1file, err := os.Open("cat_picture.jpg")
2defer file.Close()
3if err != nil {
4 panic(err)
5}
6resSendFile, statusSendFile, errSendFile := pn.SendFile().
7 Channel("my_channel").
8 Message("Look at this photo!").
9 Name("cat_picture.jpg").
10 File(file).Execute()
11fmt.Println(resSendFile, statusSendFile, errSendFile)
12fmt.Println(resSendFile.Data.ID)
1NSURL *localFileURL = ...;
2PNSendFileRequest *request = [PNSendFileRequest requestWithChannel:@"my_channel"
3 fileURL:localFileURL];
4
5[self.client sendFileWithRequest:request completion:^(PNSendFileStatus *status) {
6 if (!status.isError) {
7 /**
8 * File upload successfully completed.
9 * Uploaded file information is available here:
10 * status.data.fileIdentifier is the unique file identifier
11 * status.data.fileName is the name used to store the file
12 */
13 } else {
14 /**
15 * Handle send file error. Check the 'category' property for reasons
1// encryption is automatic if you have a crypto module configured
2
3pubnub.sendFile()
4 .channel("my_channel")
5 .fileName("cat_picture.jpg")
6 .inputStream(inputStream)
7 .message("Look at this photo!")
8 .async(result -> {
9 result.onSuccess(res -> {
10 System.out.println("send timetoken: " + res.getTimetoken());
11 System.out.println("send status: " + res.getStatus());
12 System.out.println("send fileId: " + res.getFile().getId());
13 System.out.println("send fileName: " + res.getFile().getName());
14 });
15 });
Decrypting files
The following shows how to decrypt a file using the crypto module registered in PubNub config.
- Node.js
- C#
- Go
- Objective-C
- Java
1const file = await pubnub.downloadFile({
2 channel: 'my_channel',
3 id: 'd9515cb7-48a7-41a4-9284-f4bf331bc770',
4 name: 'cat_picture.jpg'
5 });
1PNResult<PNDownloadFileResult> fileDownloadResponse = await pubnub.DownloadFile()
2 .Channel("my_channel")
3 .FileId("d9515cb7-48a7-41a4-9284-f4bf331bc770")
4 .FileName("cat_picture.jpg")
5 .ExecuteAsync();
6PNDownloadFileResult fileDownloadResult = fileDownloadResponse.Result;
7PNStatus fileDownloadStatus = fileDownloadResponse.Status;
8if (fileDownloadResult != null)
9{
10 fileDownloadResult.SaveFileToLocal(downloadUrlFileName); //saves to bin folder if no path is provided
11 Console.WriteLine(pubnub.JsonPluggableLibrary.SerializeToJsonString(fileDownloadResult.FileName));
12}
13else
14{
15 Console.WriteLine(pubnub.JsonPluggableLibrary.SerializeToJsonString(fileDownloadStatus));
1resDLFile, statusDLFile, errDLFile := pn.DownloadFile().
2 Channel("my_channel").
3 ID("d9515cb7-48a7-41a4-9284-f4bf331bc770").
4 Name("cat_picture.jpg").Execute()
5if resDLFile != nil {
6 filepathOutput := "cat_picture.jpg"
7 out, _ := os.Create(filepathOutput)
8 _, err := io.Copy(out, resDLFile.File)
9
10 if err != nil {
11 fmt.Println(err)
12 }
13}
1PNDownloadFileRequest *request = [PNDownloadFileRequest requestWithChannel:@"my_channel"
2 identifier:@"<file-identifier>"
3 name:@"cat_picture.jpg"];
4request.targetURL = ...;
5
6[self.client downloadFileWithRequest:request
7 completion:^(PNDownloadFileResult *result, PNErrorStatus *status) {
8 if (!status.isError) {
9 /**
10 * File successfully has been downloaded.
11 * status.data.location - location where downloaded file can be found
12 * status.data.temporary - whether file has been downloaded to temporary storage and
13 * will be removed on completion block return.
14 */
15 } else {
1// decryption is automatic if you have a crypto module configured
2
3pubnub.downloadFile()
4 .channel("my_channel")
5 .fileName("cat_picture.jpg")
6 .fileId("d9515cb7-48a7-41a4-9284-f4bf331bc770")
7 .async(result -> {
8 result.onSuccess(res -> {
9 System.out.println("getFile fileName: " + result.getFileName());
10 System.out.println("getFile byteStream: " + result.getByteStream());
11 });
12 });
For more examples of encrypting/decrypting files in other languages, refer to the Configuration and/or Files documentation of each SDK.
Custom encryption
Encryption and decryption are decoupled from the SDKs. You can implement your own methods.
Each SDK exposes an interface to register cryptors.
During decryption, the SDK inspects the payload and chooses the matching cryptor.
Implementation guidelines
Usage differs by SDK, but the flow is similar:
-
Implement the required interfaces (names vary). See the Crypto interfaces.
-
Create a Crypto module with your cryptor and pass it to PubNub configuration, or use it standalone for partial encryption. Refer to each SDK's Crypto module documentation.
Example custom cryptor implementation
This example uses Kotlin, but the idea is the same across SDKs.
-
Implement the
Cryptorinterface. Note that theid()method should return aByteArrayof exactly 4 bytes.1 -
Use your newly created
myCustomCryptorthat implements theCryptorinterface to instantiate aCryptoModule:
1val customCryptor = myCustomCryptor()
2val cryptoModule = CryptoModule.createNewCryptoModule(defaultCryptor = customCryptor)
Interfaces to implement
- C-Core:
pbcc_crypto.h - C#:
ICryptor.cs - Dart:
ICryptor.dart - Go:
cryptor.go - Java:
Cryptor.kt - JavaScript:
ICryptor.ts - Kotlin:
Cryptor.kt - Objective-C:
PNCryptor.h - PHP:
Cryptor.php - Python:
crypto_core.py - Ruby:
cryptor.rb - Rust:
cryptor.rs - Swift:
Cryptor.swift - Unity:
ICryptor.cs - Unreal:
PubnubCryptorInterface.h