Moderate misbehaving users as a chat administrator
Requires App Context
To work with stored user metadata, you must enable App Context for your app's keyset in the Admin Portal.
An administrator is a chat user whose Chat SDK instance was initialized with the secretKey.
Administrators can:
- Mute users on channels
- Ban users from accessing channels
Use Access Manager to enforce these restrictions. See also moderation for regular users.
Mute or ban users as an administrator
As an admin, you can mute a specific user on a channel or ban them from accessing that channel using three setRestrictions() methods.
All methods produce the same result but take different parameters depending on which object you call them on.
When an admin mutes or bans a user on a channel, a moderation event is created (of type muted or banned). You can listen to these events and, for example, remove user's membership on that channel.
Also, when an admin mutes or bans a user, an additional moderation membership is created for that user. This membership copies the ID of the channel and adds the PUBNUB_INTERNAL_MODERATION_ prefix to it, even though no new channel gets created for that purpose. This moderation membership stores information about the user's current mute and ban restrictions under the custom property.
The reason behind creating an additional moderation membership was to have an object that could be secured with Access Manager and made inaccessible to users. The standard membership object couldn't serve this purpose as it stores info on the users' lastReadMessageTimetoken custom data that users should access to be able to see unread messages on channels.
The additional membership is created only for the moderation purposes - when fetching all channel memberships for a given user with the getMemberships() method, you won't see the moderation membership as Chat SDK filters it out automatically with App Context Filtering Language.
When you lift restrictions on the user (unmute or unban them), the moderation membership is removed and a moderation event of type lifted is created.
To learn if a user is muted on a given channel or banned, use the Chat SDK methods to check moderation restrictions.
Requires Secret Key authentication
Mute and ban restrictions for the client devices should be set by servers initializing Chat SDK with a Secret Key (available on the Admin Portal on your app's keyset).
The secretKey should only be used within a secure server and never exposed to client devices. If the secretKey is ever compromised, it can be an extreme security risk to your application. If you suspect your secretKey has been compromised, you can generate a new secretKey for the existing PubNub keyset on the Admin Portal.
Method signature
These methods take the following parameters:
-
setRestrictions()(on theChatobject)1chat.setRestrictions(
2 restriction: Restriction
3): PNFuture<Unit>Definition of the
Restrictionclass:1class Restriction(
2 val userId: String,
3 val channelId: String,
4 val ban: Boolean = false,
5 val mute: Boolean = false,
6 val reason: String?
7) -
setRestrictions()(on theUserobject)1user.setRestrictions(
2 channel: Channel,
3 ban: Boolean = false,
4 mute: Boolean = false,
5 reason: String?,
6): PNFuture<Unit> -
setRestrictions()(on theChannelobject)1channel.setRestrictions(
2 user: User,
3 ban: Boolean = false,
4 mute: Boolean = false,
5 reason: String?
6): PNFuture<Unit>
Input
| Parameter | Required for Chat | Required for User | Required for Channel | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
userIdType: StringDefault: n/a | Yes | No | No | Unique User ID that becomes your app's current user. It's a string of up to 92 characters that identifies a single client (end user, device, or server) that connects to PubNub. Based on User ID, PubNub calculates pricing for your apps' usage. User ID should be persisted and remain unchanged. If you don't set userId, you won't be able to connect to PubNub. In this method, userId stands for the user that you want to mute or ban. |
channelIdType: StringDefault: n/a | Yes | No | No | ID of the channel on/from which the user should be muted or banned. |
channelType: ChannelDefault: n/a | No | Yes | No | Channel object on/from which the user should be muted or banned. |
userType: UserDefault: n/a | No | No | Yes | User object to be muted or banned. |
banType: BooleanDefault: false | No | No | No | Value that represents the user's moderation restrictions. Set to true to ban the user from the channel or to false to unban them. |
muteType: BooleanDefault: false | No | No | No | Value that represents the user's moderation restrictions. Set to true to mute the user on the channel or to false to unmute them. |
reasonType: StringDefault: n/a | No | No | No | Reason why you want to ban or mute the user. |
Output
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
PNFuture<Unit> | Function that returns an instance of PNFuture that will be completed with Unit when the setRestrictions operation is completed. |
Sample code
Mute
Mute support_agent_15 on the support channel.
-
setRestrictions()(on theChatobject)
show all 37 lines1// reference the "chat" object and invoke the "getUser()" method
2chat.getUser("support_agent_15").async { userResult ->
3 userResult.onSuccess { user ->
4 if (user != null) {
5 // get the "support" channel
6 chat.getChannel("support").async { channelResult ->
7 channelResult.onSuccess { channel ->
8 if (channel != null) {
9 // create a Restriction object to mute the user on the channel
10 val restriction = Restriction(
11 userId = user.id,
12 channelId = channel.id,
13 mute = true
14 )
15 -
setRestrictions()(on theUserobject)
show all 30 lines1// reference the "chat" object and invoke the "getUser()" method
2chat.getUser("support_agent_15").async { userResult ->
3 userResult.onSuccess { user ->
4 if (user != null) {
5 // get the "support" channel
6 chat.getChannel("support").async { channelResult ->
7 channelResult.onSuccess { channel ->
8 if (channel != null) {
9 // set the restriction using the User object
10 user.setRestrictions(channel, mute = true).async { restrictionResult ->
11 restrictionResult.onSuccess {
12 // handle success
13 }.onFailure {
14 // handle failure
15 } -
setRestrictions()(on theChannelobject)
show all 30 lines1// reference the "chat" object and invoke the "getUser()" method
2chat.getUser("support_agent_15").async { userResult ->
3 userResult.onSuccess { user ->
4 if (user != null) {
5 // get the "support" channel
6 chat.getChannel("support").async { channelResult ->
7 channelResult.onSuccess { channel ->
8 if (channel != null) {
9 // set the restriction using the Channel object
10 channel.setRestrictions(user, mute = true).async { restrictionResult ->
11 restrictionResult.onSuccess {
12 // handle success
13 }.onFailure {
14 // handle failure
15 }
Ban
Ban support_agent_15 from the support channel.
-
setRestrictions()(on theChatobject)
show all 37 lines1// reference the "chat" object and invoke the "getUser()" method
2chat.getUser("support_agent_15").async { userResult ->
3 userResult.onSuccess { user ->
4 if (user != null) {
5 // get the "support" channel
6 chat.getChannel("support").async { channelResult ->
7 channelResult.onSuccess { channel ->
8 if (channel != null) {
9 // create a Restriction object to ban the user on the channel
10 val restriction = Restriction(
11 userId = user.id,
12 channelId = channel.id,
13 ban = true
14 )
15 -
setRestrictions()(on theUserobject)
show all 30 lines1// reference the "chat" object and invoke the "getUser()" method
2chat.getUser("support_agent_15").async { userResult ->
3 userResult.onSuccess { user ->
4 if (user != null) {
5 // get the "support" channel
6 chat.getChannel("support").async { channelResult ->
7 channelResult.onSuccess { channel ->
8 if (channel != null) {
9 // set the restriction using the User object
10 user.setRestrictions(channel, ban = true).async { restrictionResult ->
11 restrictionResult.onSuccess {
12 // handle success
13 }.onFailure {
14 // handle failure
15 } -
setRestrictions()(on theChannelobject)
show all 30 lines1// reference the "chat" object and invoke the "getUser()" method
2chat.getUser("support_agent_15").async { userResult ->
3 userResult.onSuccess { user ->
4 if (user != null) {
5 // get the "support" channel
6 chat.getChannel("support").async { channelResult ->
7 channelResult.onSuccess { channel ->
8 if (channel != null) {
9 // set the restriction using the Channel object
10 channel.setRestrictions(user, ban = true).async { restrictionResult ->
11 restrictionResult.onSuccess {
12 // handle success
13 }.onFailure {
14 // handle failure
15 }
Check restrictions
One user on one channel
Check if there are any mute or ban restrictions set for a user on one channel using the getChannelRestrictions() and getUserRestrictions() methods.
Method signature
These methods take the following parameters:
-
getChannelRestrictions()1user.getChannelRestrictions(channel: Channel): PNFuture<Restriction> -
getUserRestrictions()1channel.getUserRestrictions(user: User): PNFuture<Restriction>
Input
| Parameter | Required in getChannelRestrictions() | Required in getUserRestrictions() | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
channelType: ChannelDefault: n/a | Yes | No | Channel object on/from which the user can be muted or banned. |
userType: UserDefault: n/a | No | Yes | User object that can be muted or banned. |
Output
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
PNFuture<Restriction> | PNFuture containing the Restriction object with these properties: userId, channelId, ban mute, and reason. |
Sample code
Check if the user support_agent_15 has any restrictions set on the support channel.
-
getChannelRestrictions()
show all 30 lines1// reference the "chat" object and invoke the "getUser()" method
2chat.getUser("support_agent_15").async { userResult ->
3 userResult.onSuccess { user ->
4 if (user != null) {
5 // get the "support" channel
6 chat.getChannel("support").async { channelResult ->
7 channelResult.onSuccess { channel ->
8 if (channel != null) {
9 // get the channel restrictions for the user
10 user.getChannelRestrictions(channel).async { restrictionResult ->
11 restrictionResult.onSuccess { restriction ->
12 // handle the restriction object
13 }.onFailure {
14 // handle failure
15 } -
getUserRestrictions()
show all 30 lines1// reference the "chat" object and invoke the "getUser()" method
2chat.getUser("support_agent_15").async { userResult ->
3 userResult.onSuccess { user ->
4 if (user != null) {
5 // get the "support" channel
6 chat.getChannel("support").async { channelResult ->
7 channelResult.onSuccess { channel ->
8 if (channel != null) {
9 // get the user restrictions for the channel
10 channel.getUserRestrictions(user).async { restrictionResult ->
11 restrictionResult.onSuccess { restriction ->
12 // handle the restriction object
13 }.onFailure {
14 // handle failure
15 }
One user on all channels
Check if there are any mute or ban restrictions set for a user on all channels they are a member of using the getChannelsRestrictions() method.
Method signature
This method takes the following parameters:
1user.getChannelsRestrictions(
2 limit: Int?,
3 page: PNPage?,
4 sort: Collection<PNSortKey<PNMembershipKey>> = listOf(),
5): PNFuture<GetRestrictionsResponse>
Input
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
limitType: IntDefault: 100 | Number of objects to return in response. The default (and maximum) value is 100. |
pageType: PNPageDefault: n/a | Object used for pagination to define which previous or next result page you want to fetch. |
sortType: Collection<PNSortKey<PNMembershipKey>>Default: listOf() | Key-value pair of a property to sort by, and a sort direction. Available options are id, name, and updated. Use asc or desc to specify the sorting direction, or specify null to take the default sorting direction (ascending). For example: {name: "asc"}. By default, the items are sorted by the last updated date. |
Output
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
PNFuture<GetRestrictionsResponse> | PNFuture containing the GetRestrictionsResponse object with these properties: restrictions, next, prev, total, and status. |
Sample code
List all mute and ban restrictions set for the user support_agent_15.
1// reference the "chat" object and invoke the "getUser()" method
2chat.getUser("support_agent_15").async { result ->
3 result.onSuccess { user ->
4 if (user != null) {
5 // fetch the channel restrictions for the user
6 user.getChannelsRestrictions().async { restrictionsResult ->
7 restrictionsResult.onSuccess { getRestrictionsResponse ->
8 // process the returned restrictions
9 for (restriction in getRestrictionsResponse.restrictions) {
10 if (restriction.mute || restriction.ban) {
11 // handle the restriction object (either muted or banned)
12 println("User is restricted on channel ${restriction.channelId}: mute=${restriction.mute}, ban=${restriction.ban}")
13 }
14 }
15 }.onFailure {
All users on one channel
Check if there are any mute or ban restrictions set for user of a given channel using the getUsersRestrictions() method.
Method signature
This method takes the following parameters:
1channel.getUsersRestrictions(
2 limit: Int?,
3 page: PNPage?,
4 sort: Collection<PNSortKey<PNMemberKey>> = listOf(),
5): PNFuture<GetRestrictionsResponse>
Input
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
limitType: IntDefault: 100 | Number of objects to return in response. The default (and maximum) value is 100. |
pageType: PNPageDefault: n/a | Object used for pagination to define which previous or next result page you want to fetch. |
sortType: Collection<PNSortKey<PNMemberKey>>Default: listOf() | Key-value pair of a property to sort by, and a sort direction. Available options are id, name, and updated. Use asc or desc to specify the sorting direction, or specify null to take the default sorting direction (ascending). For example: {name: "asc"}. By default, the items are sorted by the last updated date. |
Output
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
PNFuture<GetRestrictionsResponse> | PNFuture containing the GetRestrictionsResponse object with these properties: restrictions, next, prev, total, and status. |
Sample code
List all mute and ban restrictions set for the support channel.
1// reference the "chat" object and invoke the "getChannel()" method
2chat.getChannel("support").async { result ->
3 result.onSuccess { channel ->
4 if (channel != null) {
5 // fetch the user restrictions for the channel
6 channel.getUsersRestrictions().async { restrictionsResult ->
7 restrictionsResult.onSuccess { getRestrictionsResponse ->
8 // process the returned restrictions
9 for (restriction in getRestrictionsResponse.restrictions) {
10 if (restriction.mute || restriction.ban) {
11 // handle the restriction object (either muted or banned)
12 println("User ${restriction.userId} is restricted in channel ${channel.id}: mute=${restriction.mute}, ban=${restriction.ban}")
13 }
14 }
15 }.onFailure {
Secure moderation
You could try to use only the banning or muting restrictions on client devices and enforce some UI moderation, like not displaying channels for users who are banned from them, or not displaying input field for users who are muted on a given channel so that they couldn't post a message.
Still, such solely client-side restrictions can easily be bypassed if not secured with an additional server-side logic that uses Access Manager to allow or block user's access to PubNub resources (channels and users). This server-side can also be followed by additional client-side errors that inform app users about their restrictions up front.
Client-side moderation
For more information on client-side moderation for regular chat users, refer to Moderation as user.
Server-side restrictions
It's recommended to use Access Manager alongside the Chat SDK methods and grant or revoke permissions from users based on their muting or banning restrictions.
Mute list and Access Manager
If you use Access Manager for user moderation within your chat app, and your users use the client-side mute list functionality with the syncMutedUsers parameter enabled, you must grant the Chat SDK user the following permissions:
readpermission to thePN_PRV.$currentUserId.mute1channel.update,delete, andgetpermissions for thePN_PRV.$currentUserId.mute1user.
Make sure to change $currentUserId to the user ID of the chat user that will use the mute list functionality.
For example, you could have a UI moderation dashboard (like Channel Monitor) where admins set restrictions on users by muting or banning them from specific channels. After that, you can use one of the Chat SDK methods to get moderation restrictions for users and, based on results, call the Access Manager API to either generate or revoke grant tokens for PubNub resources (channels or users).
Let's look at sample steps that use Chat SDK methods to configure a chat app, set up server permissions, listen to any permission changes in Channel Monitor UI, and invoke access grant or revoke request on the server side.
-
Enable Access Manager.
Navigate to your app's keyset in the Admin Portal and turn on the ACCESS MANAGER option.
-
Initialize Chat SDK with
token.On the frontend of your app, initialize the Chat SDK (
init()) with the token (generated by server-side code). Use it for all requests made to PubNub APIs to authenticate users in your application and grant them access to PubNub resources (other users' metadata and channels).1val userId = "your-user-id"
2val token = "token-generated-by-server-side"
3// ...
4
5Chat.init(ChatConfiguration(), PNConfiguration.builder(UserId(userId), subscribeKey = "your-subscribe-key-from-admin-portal") {
6 publishKey = "your-publish-key-from-admin-portal"
7 authToken = token
8}.build()).async {
9 it.onSuccess { chat ->
10 // ...
11 }.onFailure {
12 // unable to initialize Chat
13 }
14} -
Secure backend initialization.
On the backend, initialize the Chat SDK with the secret key
secretKeyon your servers to secure your PubNub instance.Secret key
secretKeyis a secret shared between your application's server and PubNub and it's used to administer Access Manager permissions for your client applications by signing and verifying the authenticity of messages and requests. Remember to never expose thesecretKeyto client devices.
show all 25 lines1val serverId = "auth-server"
2var token: String
3val clientUserIdValue = "clientUserId"
4// ...
5
6Chat.init(ChatConfiguration(), PNConfiguration.builder(UserId(serverId), subscribeKey = "your-subscribe-key-from-admin-portal") {
7 publishKey = "your-publish-key-from-admin-portal"
8 secretKey = "your-secret-key-from-admin-portal"
9}.build()).async {
10 it.onSuccess { chat ->
11 chat.pubNub.grantToken(
12 ttl = 1,
13 channels = listOf(ChannelGrant.name(get = true, name = "anyChannelForNow")),
14 uuids = listOf(UUIDGrant.id(id = clientUserIdValue, get = true, update = true)) // this is important
15 ).async { grantTokenResult -> -
Get user permissions.
Retrieve detailed user restrictions and convert these details into a simplified permission format where each channel is marked with whether the user can read, write, or access it, based on such restrictions as bans or mutes.
show all 24 lines1val userId: String
2// ...
3
4// Retrieve user information and channel restrictions
5chat.getUser(userId).async {
6 it.onSuccess { user ->
7 user?.getChannelsRestrictions()?.async {
8 it.onSuccess { restrictionsResponse ->
9 val grants = restrictionsResponse.restrictions.map { restriction ->
10 ChannelGrant.name(restriction.channelId,
11 read = !restriction.ban,
12 write = (!restriction.mute && !restriction.ban),
13 get = true,
14 )
15 } -
Generate authorization token.
Generate and assign an access token reflecting the user's permissions.
The token contains information about which channels the user can access and how (read/write), and it's configured with a specific validity period. This token serves as a key for users to interact with the application according to their permissions.
Operation-to-permission mapping
Read the Permissions document for a complete list of available operations that users can do with PubNub resources in apps created with the Chat SDK.
1val restrictionGrants: List<ChannelGrant>
2// ...
3
4// Set up parameters for the authorization token
5chat.pubNub.grantToken(ttl = 43200, authorizedUUID = userId, channels =
6 listOf(
7 ChannelGrant.pattern(".*", get = true, read = true, write = true),
8 ) + restrictionGrants,
9 uuids = listOf(
10 UUIDGrant.id(userId, get = true, update = true)
11 )
12)Set short TTLs
You can mute or ban a user for an indefinite amount of time, but you can unmute/unban them at any time. To make sure that the permissions set with Access Manager reflect the most up-to-date muting/banning restrictions on the client-side, it's recommended to set short-lived tokens (TTLs) for grant calls (valid for seconds and minutes rather than hours or days). Alternatively, if new muting/banning restrictions are set on the frontend side of your app, you can revoke Access Manager permissions on the backend using the
chat.sdk.revokeToken()method. -
Listen for moderation events.
All
moderationevents generated by muting and banning actions are sent to a singlePUBNUB_INTERNAL_MODERATION.[user_id]channel. You can listen to these events through Events & Actions in the Admin Portal.To do that, create a new event listener, choose Messages as event source, and configure the event listener as follows:
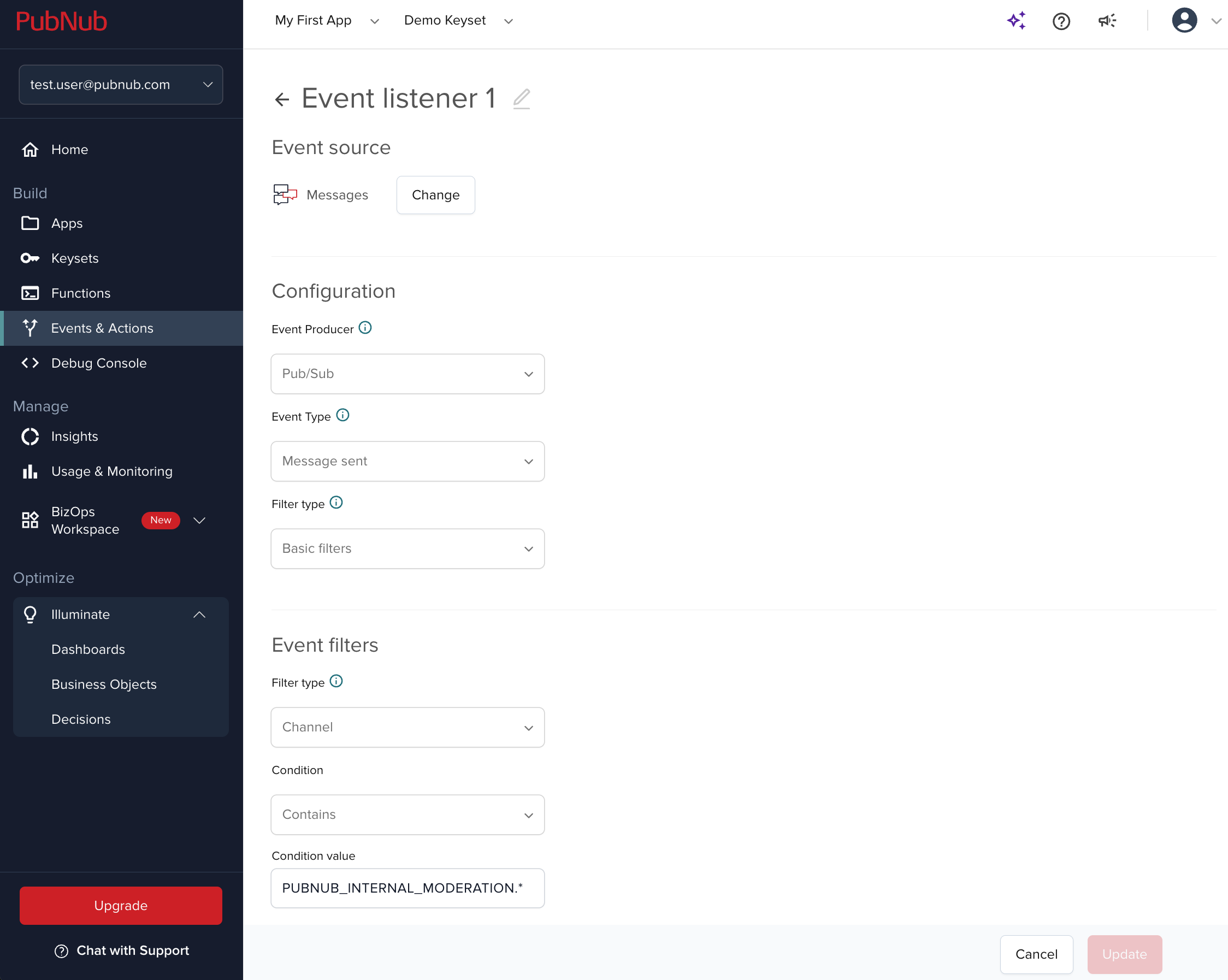
-
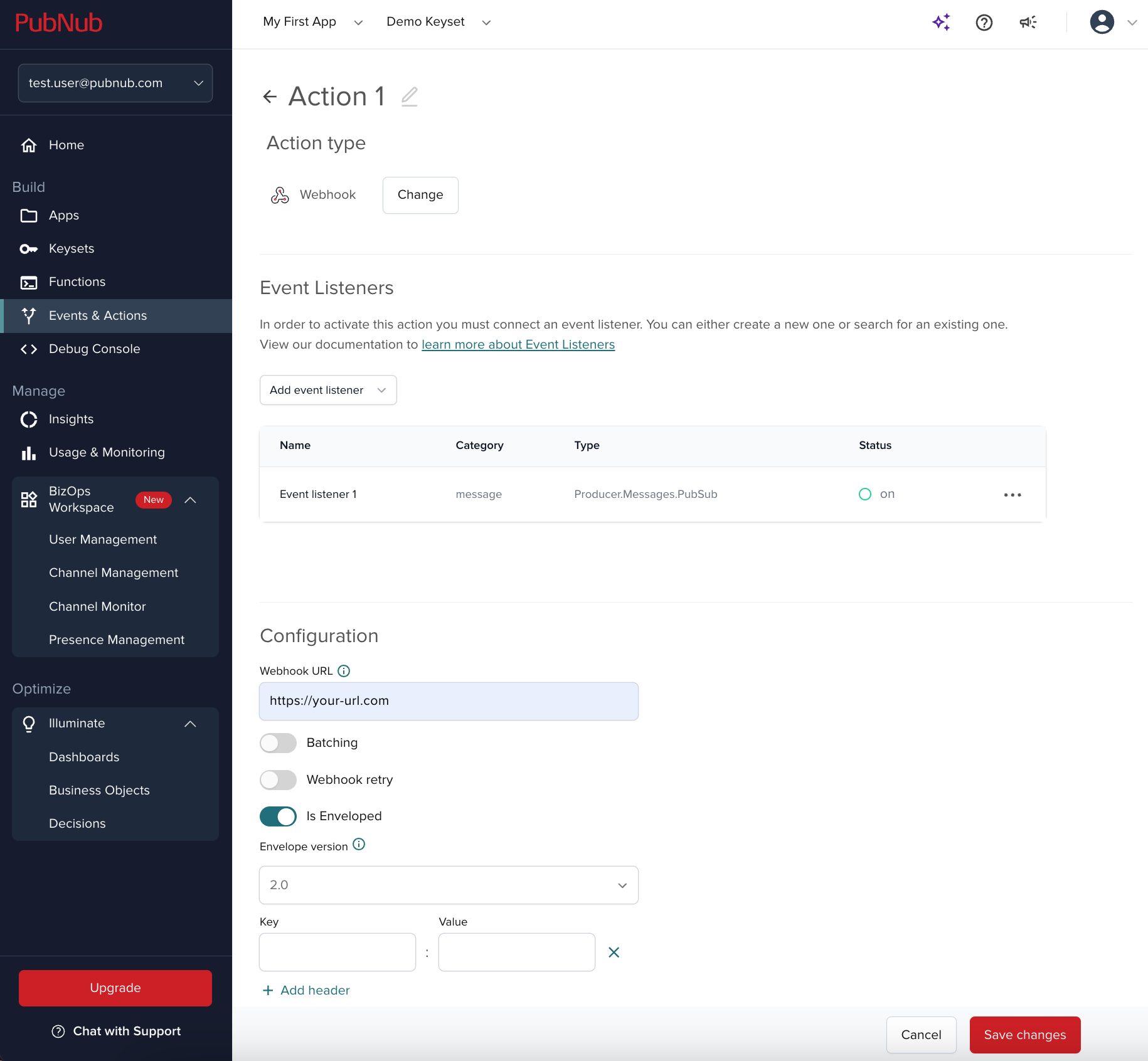
Act on moderation events.
Create a Webhook type of action in Events & Actions where you must specify the URL of the server you want to hit for authentication token changes each time a new
moderationevent is generated.Link the action to the previously created listener.
Client-side restrictions
Once you enable and define server-side permissions with Access Manager, you can be sure that your muting and banning restrictions are always enforced.
Client-side moderation
For more information on working with client-side restrictions for regular chat users, refer to Client-side restrictions.
Listen to moderation events
As an admin of your chat app, you can use the listenForEvents() method to send notifications to the affected user when you mute or ban them on a channel, or to remove user channel membership each time they are banned.
Events documentation
To read more about the events of type moderation, refer to the Chat events documentation.
Method signature
This method has the following parameters:
1fun <reified T : EventContent> listenForEvents(
2 channel: PUBNUB_INTERNAL_MODERATION.${userId},
3 customMethod: EmitEventMethod?,
4 noinline callback: (event: Event<T>) -> Unit
5): AutoCloseable
Input
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
T *Type: reified T : EventContentDefault: n/a | Reified type parameter bounded by the EventContent interface, allowing access to type information at runtime. |
channel *Type: PUBNUB_INTERNAL_MODERATION.${userId}Default: n/a | Channel to listen for new moderation events. It is the user's channel (ID of the moderated user) which you want to get moderation events from. |
customMethodType: StringDefault: n/a | An optional custom method for emitting events. If not provided, defaults to null. |
callback *Type: noinline (event: Event<T>) -> UnitDefault: n/a | A lambda function that is called with an Event<T> as its parameter. It defines the custom behavior to be executed whenever an moderation event type is detected on the specified channel. |
Output
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
AutoCloseable | Interface that lets you stop receiving moderation-related updates (moderation events) by invoking the close() method. |
Sample code
Send a moderation event to the muted user.
1val unsubscribe = chat.listenForEvents<EventContent.Moderation>(
2 channel = "support", // Use the correct parameter name
3 customMethod = null // Explicitly specify null for the custom method
4) { event: Event<EventContent.Moderation> ->
5 if (event.payload.restriction == RestrictionType.MUTE) {
6 println("You were muted on channel ${event.payload.channelId}")
7 }
8}
9
10// Remember to handle unsubscription if needed
11unsubscribe.close()