Functions v1
Functions let you run code or use integrations without running your own servers or adding latency from external callouts. Your code runs in PubNub's environment for low-latency, real-time processing.
PubNub offers Functions in two versions (v1 and v2) that differ in terms of scope, terminology, UI flow on the Admin Portal, and library or REST API access.
Function versions
This document details the UI for Functions v1 that are accessible for PubNub users who created Functions before v2 was introduced. To learn about the differences between both versions, refer to the Functions v1 vs. v2 comparison.
The steps for creating a Function also differ depending on the version. For details, refer to Development Guidelines v2 and Development Guidelines v1.
Modules
To create a Function, first create a Module.
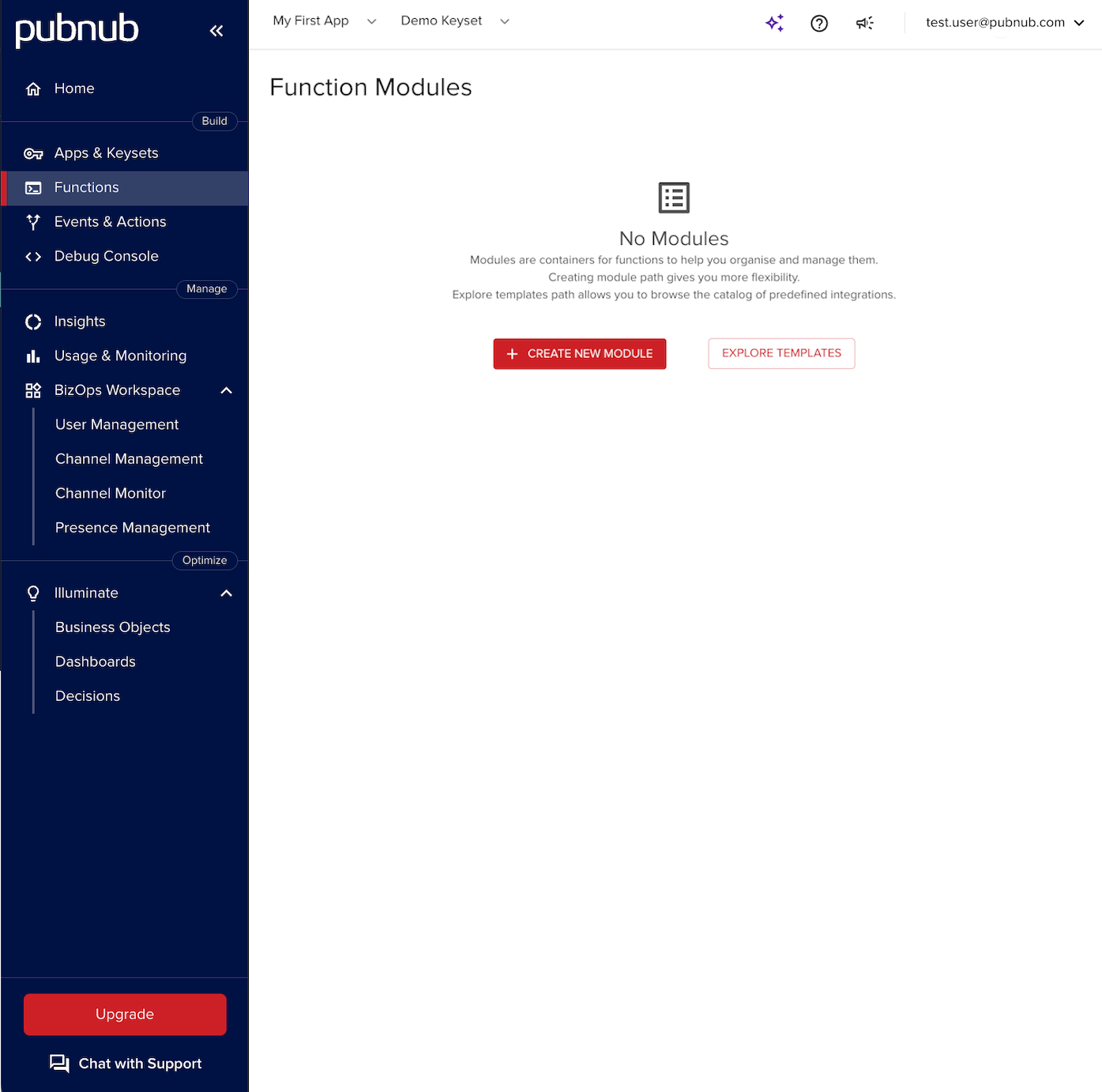
To create a Module:
-
Choose an app with a corresponding keyset.
-
Click + Create New Module.
-
Fill in the mandatory Name field and the optional Description field.
For information on how to create Functions, refer to the Development Guide.
Statistics
Select the Module to view all Functions created in it.

You can see whether a Module is Running or Stopped, and key metrics for its Functions:

| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Total | The number of created functions inside the module. |
| Running | All functions in the module are running and operational. |
| Stopped | None of the functions in the module are running. Messages will pass through the PubNub network without triggering your saved Functions. |
| Pending | Functions in the module are being started. This is a transient state and the module may remain in this state for up to 20 seconds. |
Module states:
| State | Definition |
|---|---|
Stopped | None of the Functions in the Module are running. Messages will pass through the PubNub network without triggering your saved Functions. |
Running | All Functions in the Module are running and operational. |
Pending | The Functions in the Module are being started. This is a transient state, and the Module may remain in this state for up to 20 seconds. |
Stopping | The Module is being stopped. Like the Pending state, this is a transient state, and the Module may remain in the Stopping state for few seconds. |
Failed | One or more Functions in the Module failed to run because of an error, and all Functions are stopped. Check the logs for more information. |
Functions overview
This section shows all Functions available in a Module:

| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | Name of your function. |
| Event | Event type tied to your function. |
| Channels/Path/Interval | Configuration parameters of your function. |
| State | State of your function. Refer to the previous table to view available states. |
Third-party services integration
You can also use third-party integrations, such as language translation, sentiment analysis, SMS, text-to-speech, and content moderation.
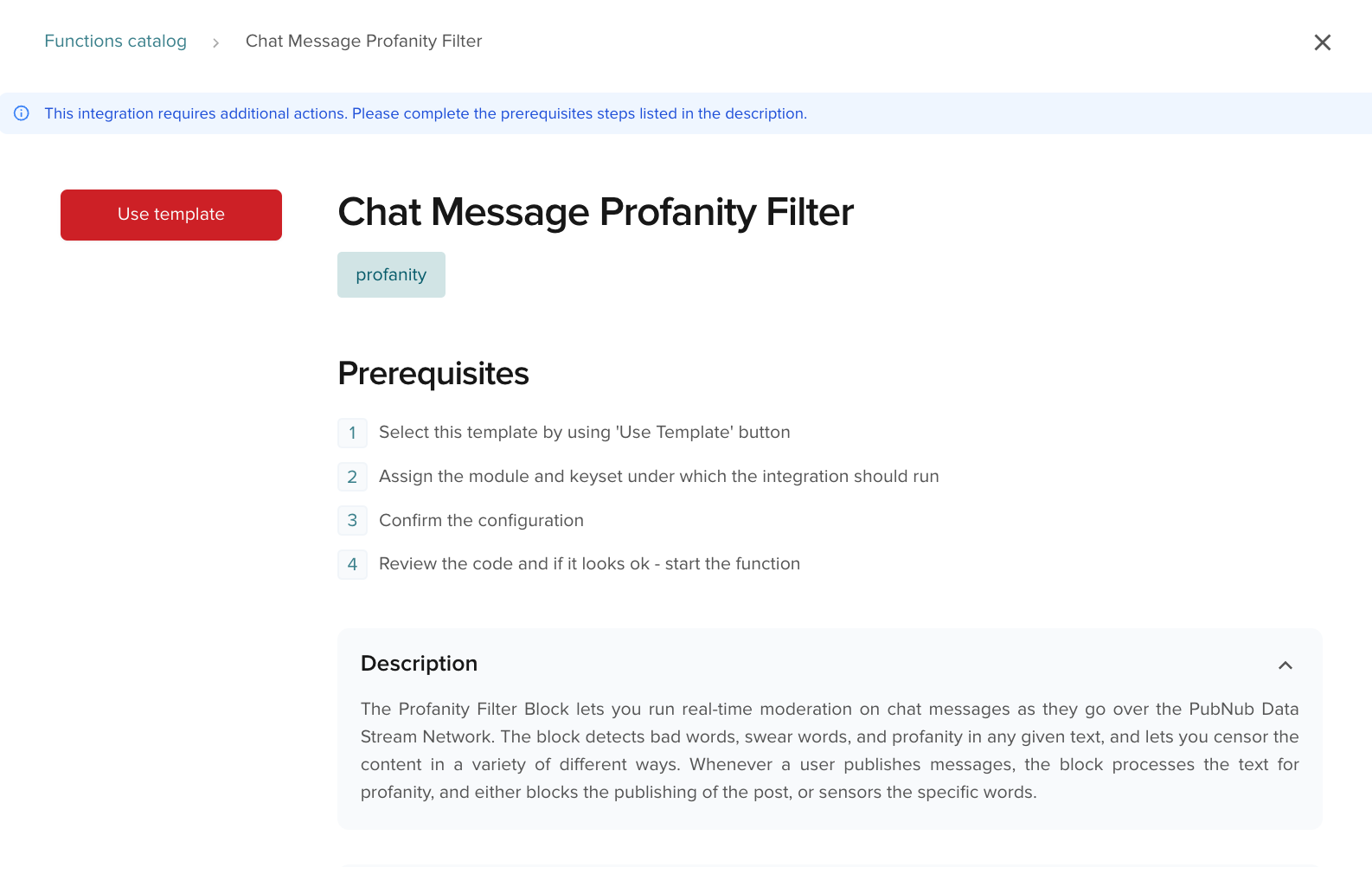
Click Explore Templates in a Module to open the Functions integrations catalog in the Admin Portal.
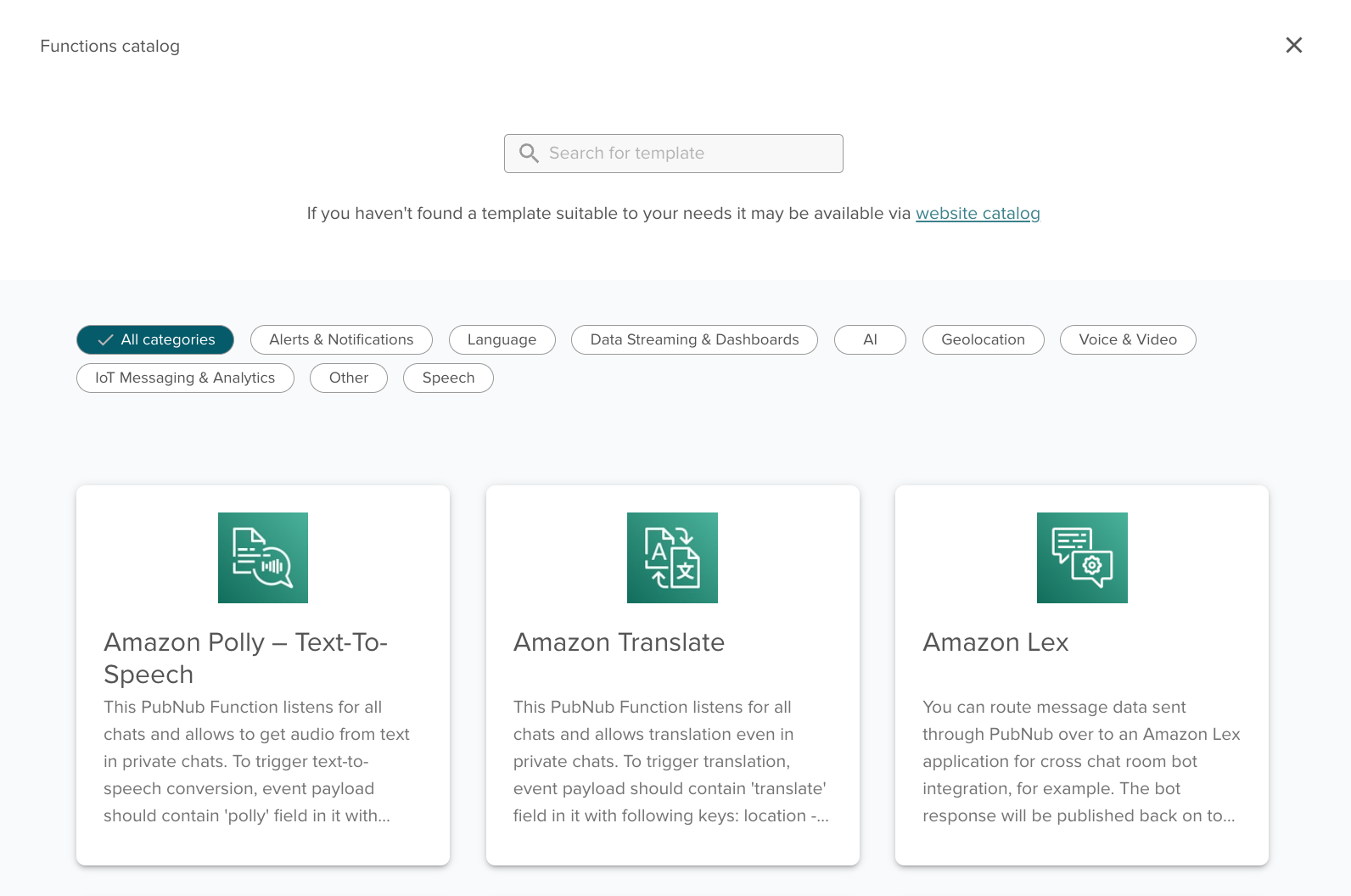
If you can't find a service that fits, browse the full Integrations catalog outside the Admin Portal. When you choose an integration, click Use template and follow the wizard.
Function configuration view
Click a Function in the Module to open the configuration view. There you can configure the Function, edit code, rename it, choose the channel, and test. The view has these sections:
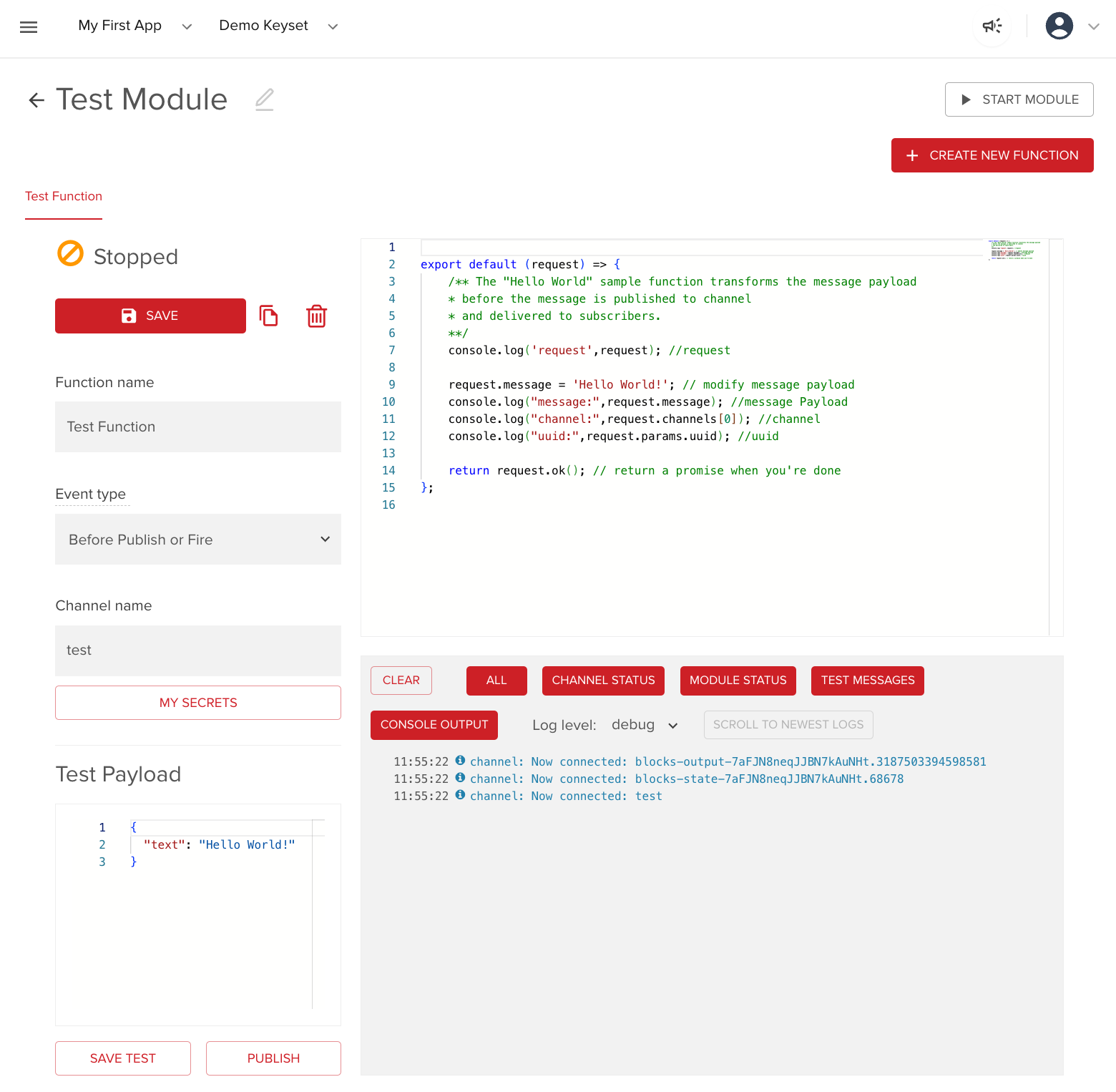
Function parameters
You can configure these parts of your Function:
| Name | Configurable items |
|---|---|
| Function name | Current name of the function. |
| Event type | Event type of the currently selected function. |
| Channel | Channel the function runs on. |
| URI path | A suffix added to the full URL where your On Request Function is triggered. For example, if you set the URI path to hello, your Function triggers on https://ps.pndsn.com/v1/blocks/sub-key/{your-sub-key}/hello. Only for the On Request event type. (URI = Uniform Resource Identifier) |
| Test Payload | Test message payload. Its initial structure changes based on the event type of the selected function. You can change the payload to suit your needs. |
| Add REST parameters | Additional REST parameters. Only available in the On Request event type. |
| Add headers | Additional headers. Only available in the On Request event type. |
| Interval | Interval for the function to trigger. Can be set between 10000 and 3600000 milliseconds. Only available in the On Interval event type. |
| My Secrets | Credentials configuration. You can store secrets and use them in the function body. |
Code editor
Use this editor to create or modify your Function's code. The example code depends on the Function's event type you chose when creating it. If you change the event type later, the example code doesn't refresh.
For details on creating Functions, see Creating a function.
Wildcard channels
In the code editor, use a specific channel. Wildcards aren't supported there.
Console view
Displays debug information about your Module and Function. You can show all filters, clear the console, or filter by selecting one or more of the following:
| Filter name | Displayed information |
|---|---|
| Channel status | The channel your function runs on. |
| Module status | The deployment status and deployment regions. |
| Test messages | Type and body of published messages set in the Test payload section. |
| Console output | The output logged to the console from within your function body. |
Export logs through Events & Actions
Any running Function publishes logs to an internal blocks-output-* channel, like blocks-output-NSPiAuYKsWSxJl4yBn30.
You can find this channel name in the Console output:
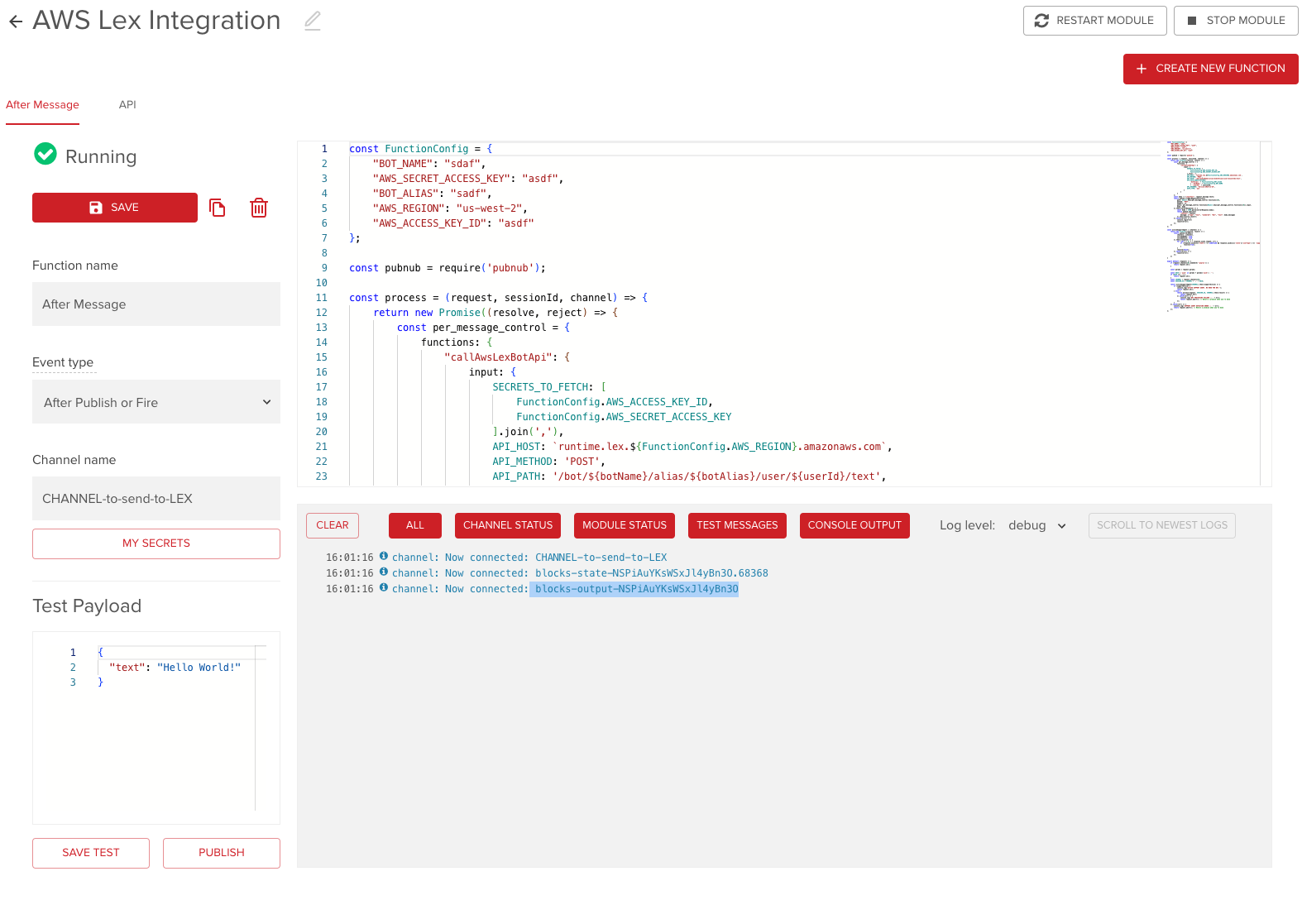
The channel keeps the last 250 lines; new logs overwrite older ones.
To retain logs longer, use Events & Actions to export logs to an external service with the Webhook or S3 action.
To do that, follow these steps:
-
Set up an event listener to listen for events on the internal channel. Provide the following configuration and enter the correct
blocks-output-*channel from the Console output in the Condition value field.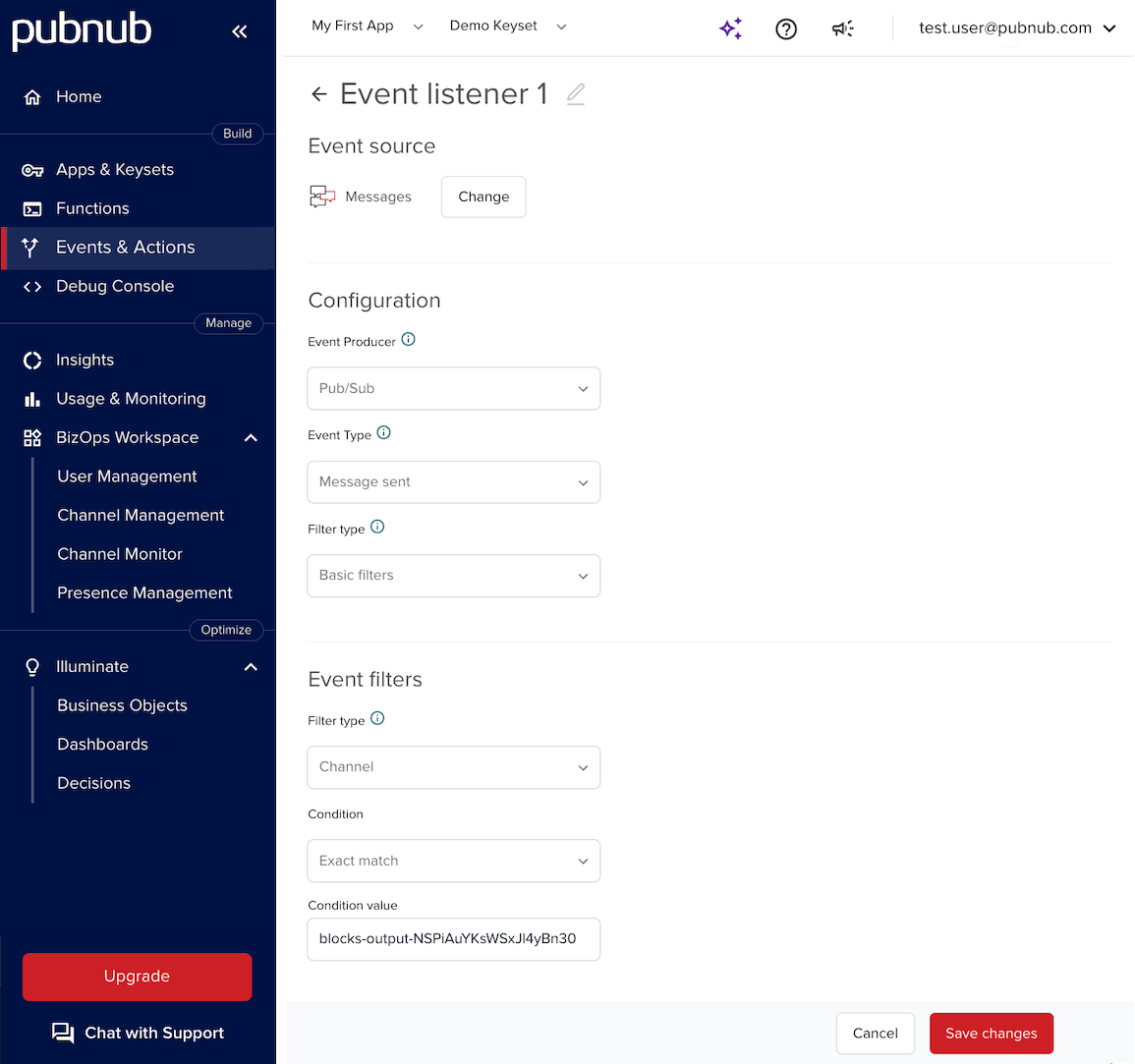
-
Create either a Webhook or S3 action and add the created event listener to it.
When configuring this action, you can use the Batching feature to send multiple events in a single request.